- Home
- Product
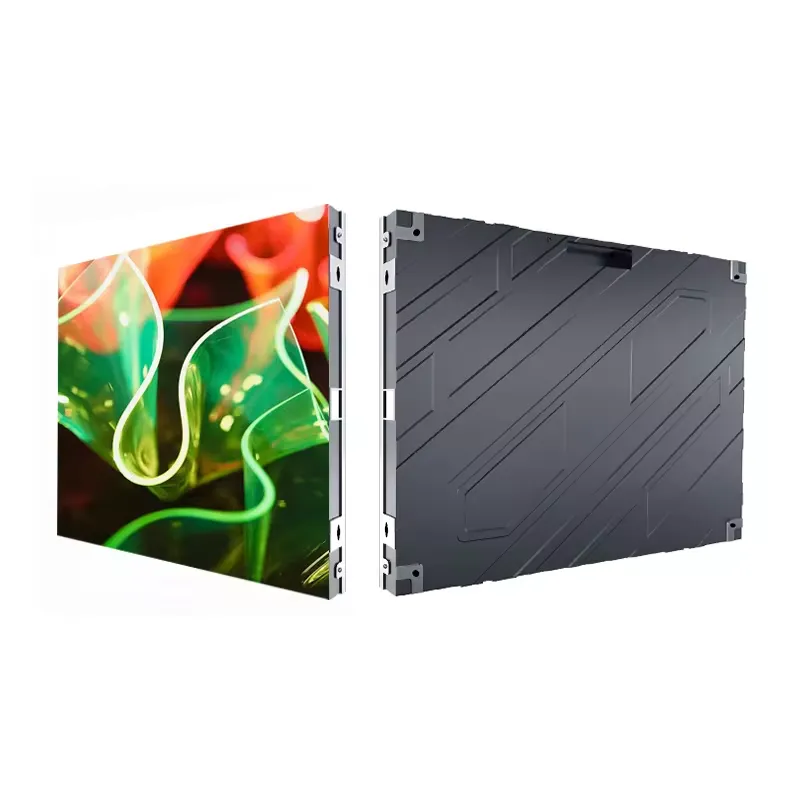

Indoor LED Video Walls
Suitable for various kinds of indoor applications

Temp Sensors Displays
It used where temperature and humidity monitoring are requires
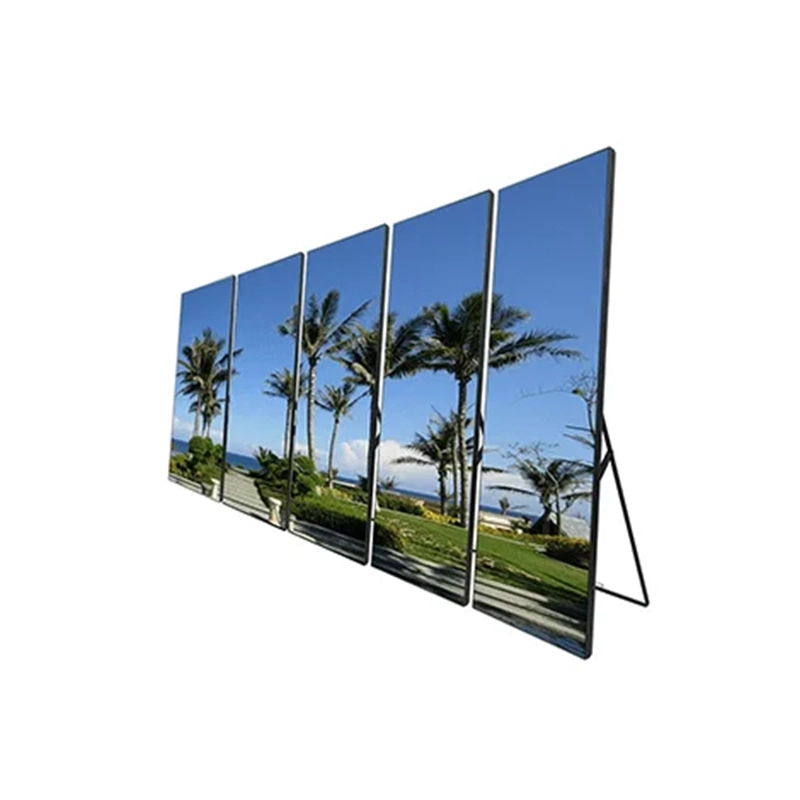

Standy Video Walls
suitable for various kinds of indoor applications
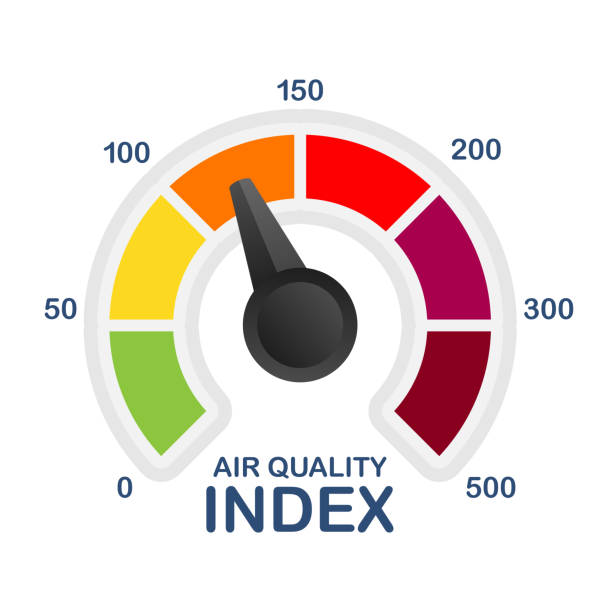
Air Quality Index
It used to display the complete air quality index

Outdoor LED Video Walls
Suitable for various kinds of Outdoor Applications
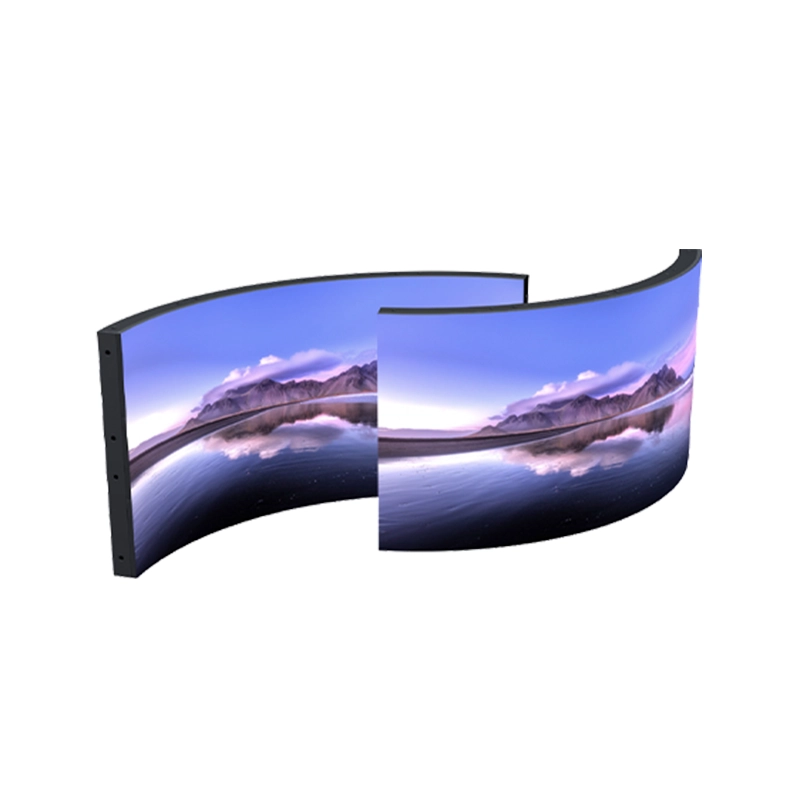
Curve Video Wall
Implemented on convex or concave side, based on requirements.
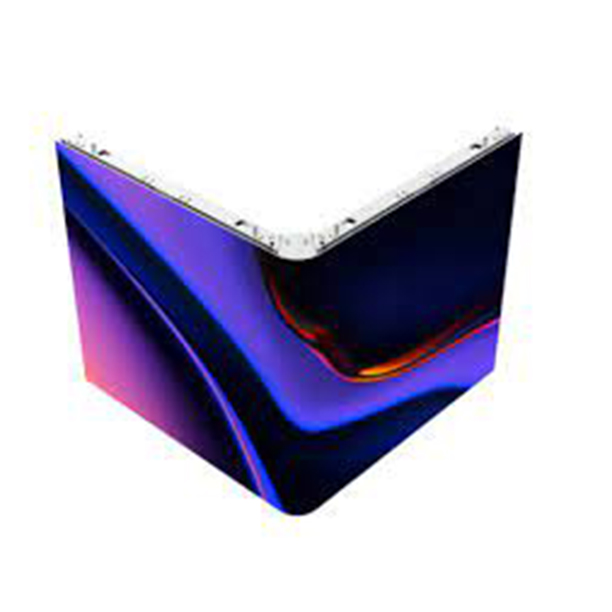
Corner Video Walls
It could be Outdoor LED Video Wall or Indoor Led Video Wall
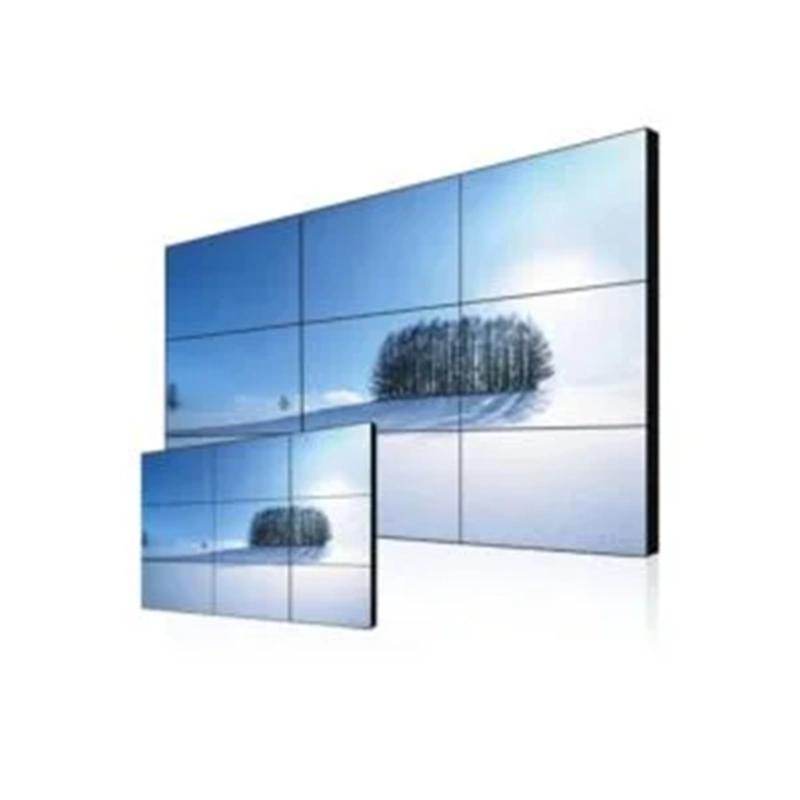

Rental Video Walls
Suitable for various purposes depending on requirements

Scrolling Board
These LED display screen to convey a message.
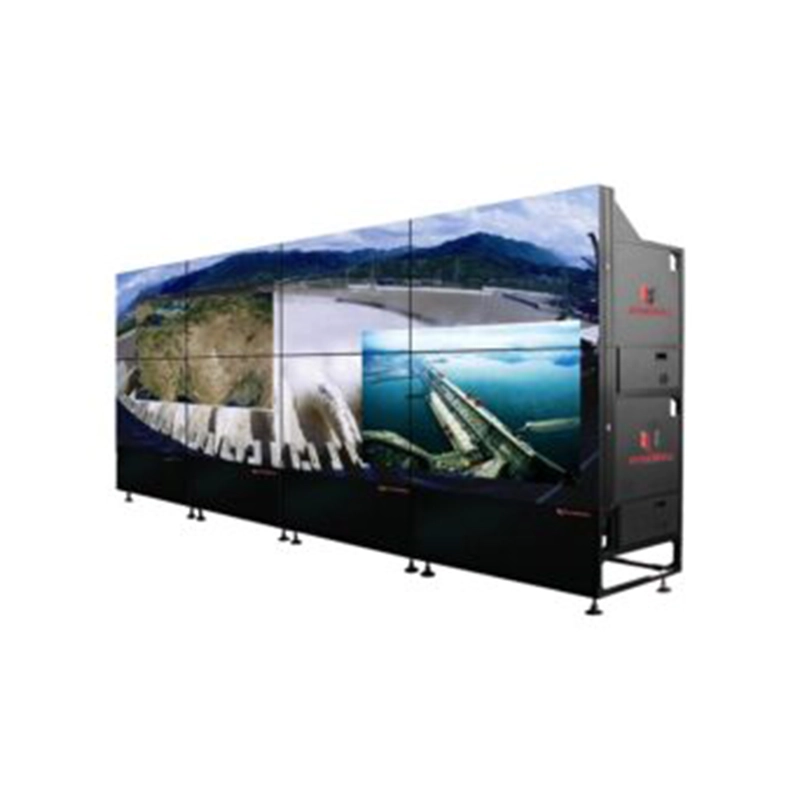

PRO Series Video Wall
Suitable for various kinds of Curve video wall
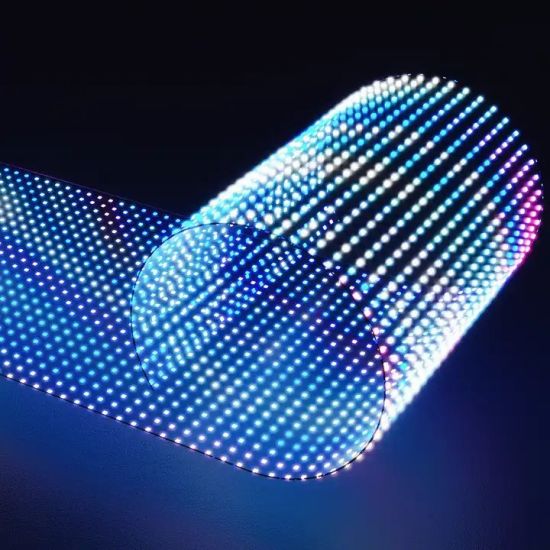
Transparent Video Walls
Almost invisible appearance with effective visualization
- Application
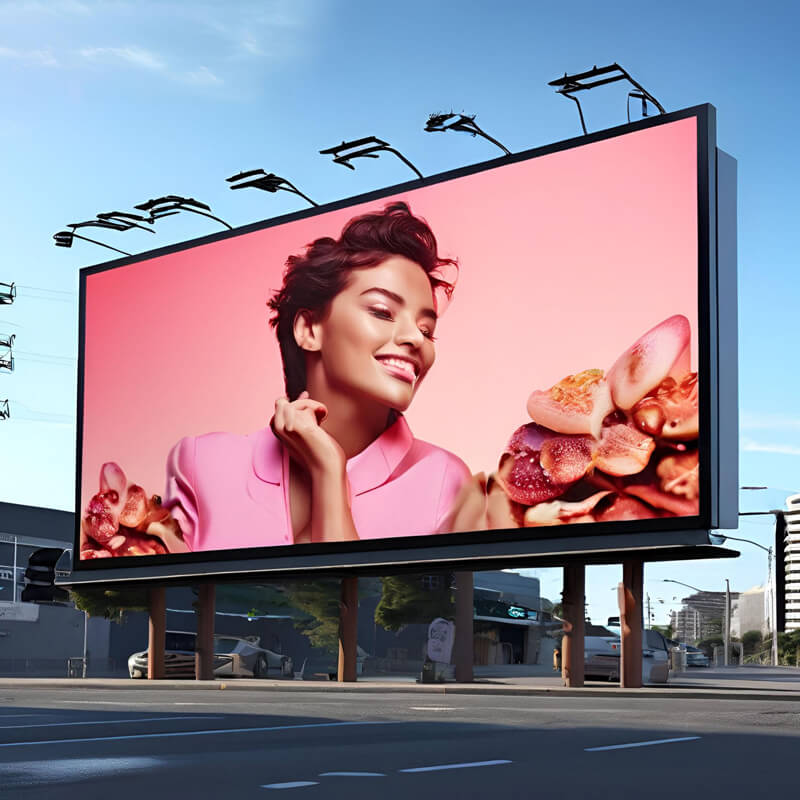

Outdoor Advertisement
Suitable for various kinds of indoor applications
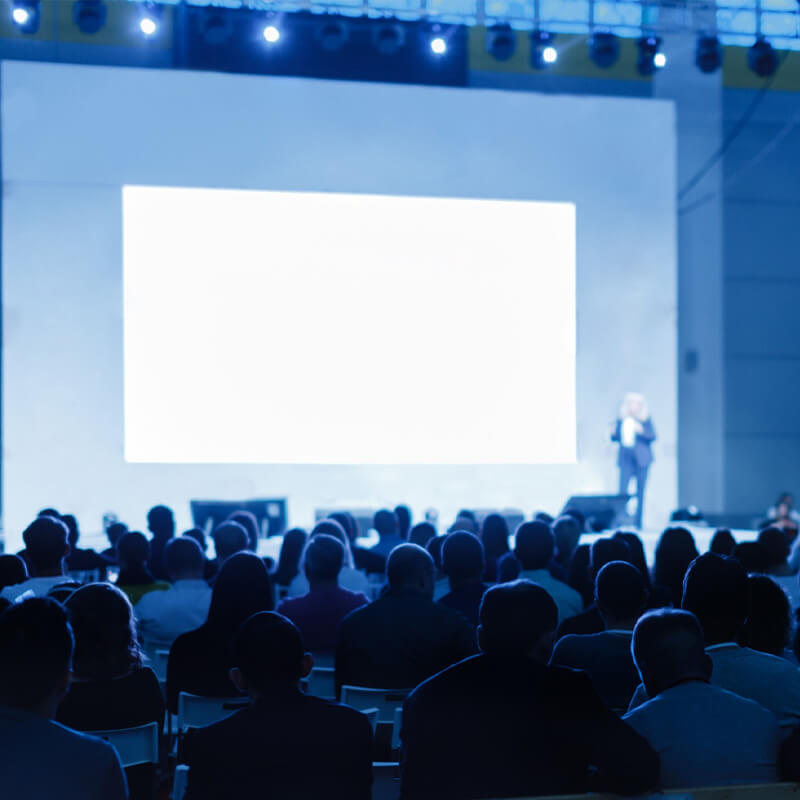

Conferences
Suitable for various purposes depending on requirements
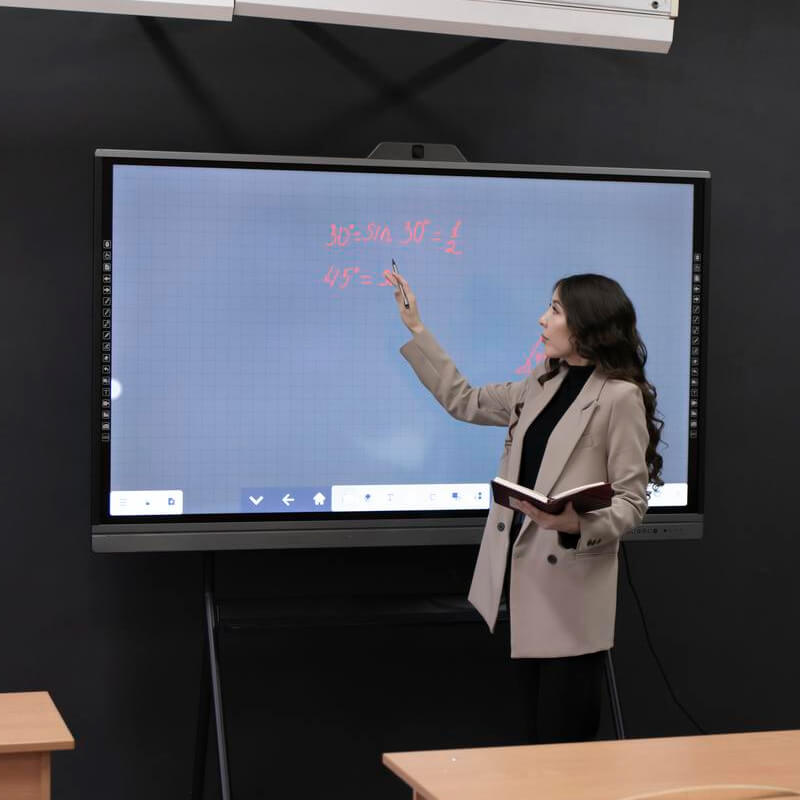

Education
suitable for various kinds of indoor applications

Indoor Advertisement
Suitable for various kinds of Outdoor Applications
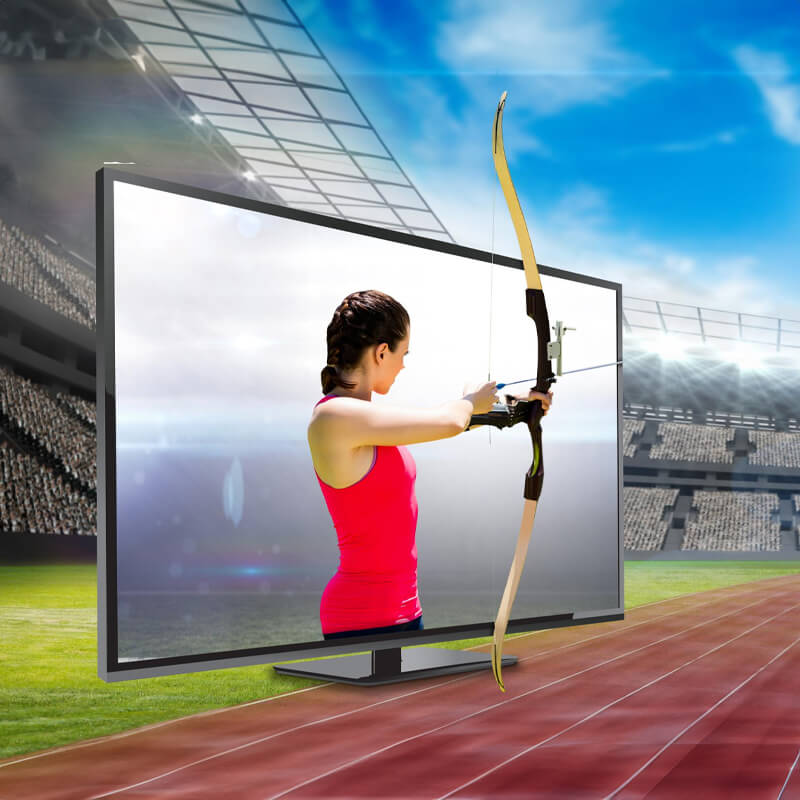

Sports
Implemented on convex or concave side, based on requirements.

Event Organiser
It could be Outdoor LED Video Wall or Indoor Led Video Wall

Meeting Room
These LED display screen to convey a message.

Display Standee
Suitable for various kinds of Curve video wall

Health Care
A display that allows user to experience 3D effects
- Knowledge Centre
- Blogs
- Gallery
- About Us
Address
- No.10, KNO -203/210/211 Kattigehalli Village, Yelahanka, Bengaluru, Karnataka 562114
- +91 9108319220 / 6364336452
- contact@novaviewledscreen.com
Follow Us

Copyright © 2026 Novaviewledscreen | All rights reserved.
